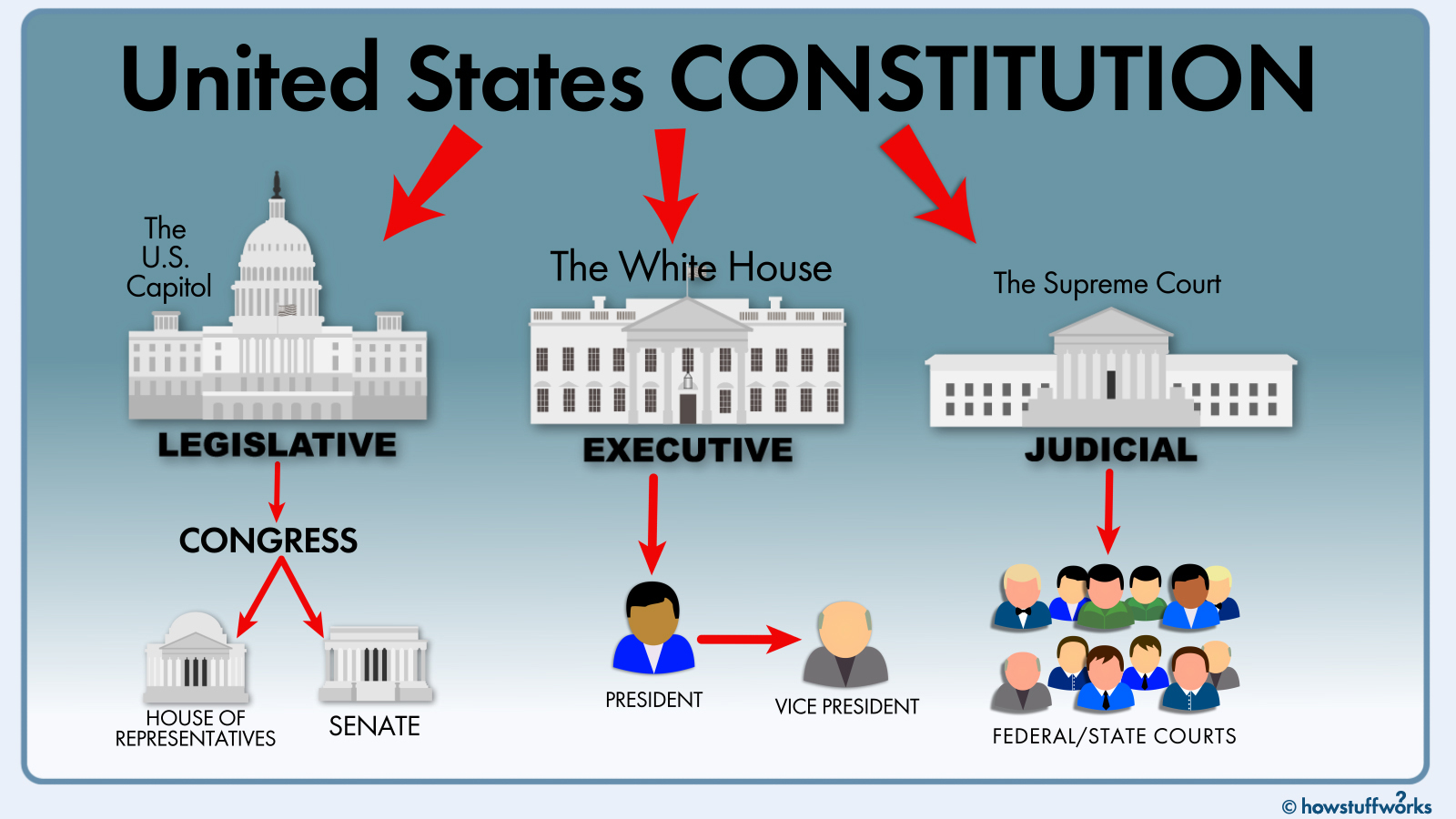
United States Government: Learn about the three branches of government (Executive, Legislative, Judicial), the President, Congress, and the Supreme Court.
Executive Branch:
- The President: The President is the head of state and government and serves as the Commander-in-Chief of the U.S. armed forces. They are responsible for enforcing federal laws, appointing federal executive officials, and conducting foreign affairs.
- Vice President: The Vice President supports the President's duties and assumes the role of President if the President is unable to carry out their duties.
Legislative Branch:
- Congress: The United States Congress is the legislative body and is bicameral, consisting of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives.
- Senate: The Senate has 100 members, two from each state, serving six-year terms. They have responsibilities such as ratifying treaties and confirming presidential appointments, including Supreme Court justices.
- House of Representatives: The House has 435 members, with the number per state determined by population. They serve two-year terms and play a vital role in introducing and passing legislation.
Judicial Branch:
- Supreme Court: The Supreme Court is the highest court in the federal judiciary. It consists of nine justices, led by the Chief Justice of the United States. The Court interprets the Constitution and federal laws, ensuring they align with the country's principles.
- Federal Courts: Apart from the Supreme Court, there are lower federal courts, including Circuit Courts of Appeals and District Courts, that hear cases at the federal level.
These branches operate through a system of checks and balances, ensuring that no single branch gains excessive power. For example, the President can veto legislation passed by Congress, but Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds majority vote. The Supreme Court can declare laws or executive actions unconstitutional, but the President nominates Supreme Court justices, subject to Senate approval.
The United States Government's structure is based on the U.S. Constitution, which serves as the foundation of the country's laws and principles. The Constitution outlines the powers and limitations of each branch, fostering a democratic system of governance.
If you have any specific questions or need more information about any aspect of the U.S. government, feel free to ask!